In the first large-scale global study of the genetics of major depression in participants of diverse ancestry groups, researchers discovered more than 50 new genetic loci (a locus is a specific position on a chromosome) and 205 novel genes associated with depression. The study also demonstrates the potential for drug repurposing, as NDUFAF3 – one…
Category: Biology
How Lactobacillus Helps Support Stress Reselience
Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have revealed how Lactobacillus, a bacterium found in fermented foods and yogurt, helps the body manage stress and may help prevent depression and anxiety. The findings pave the way for new therapies to treat anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions. According to UVA researcher Alban…
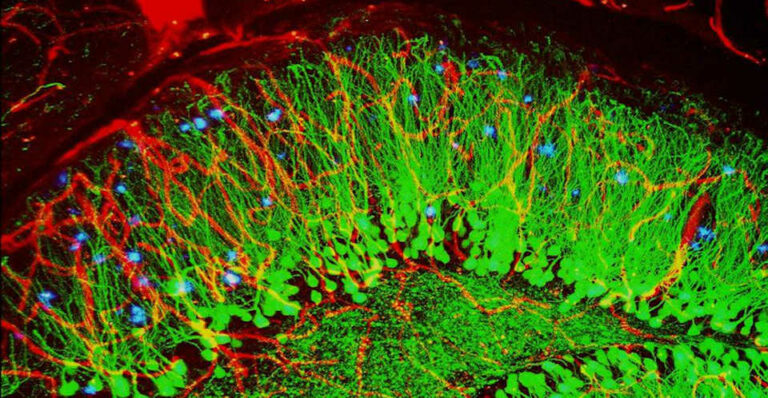
KDM5A Autism-linked Gene May Alter Hippocampus Cell Identity
A gene that University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center researchers previously associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) now appears to play a crucial role in directing hippocampus cells toward their final identities, according to a new study by the same group. Potentially, the findings may pave the way for novel treatments of this pervasive neurodevelopmental…
Small Eye Movements Play Big Role in Spatial Vision
Our eyes are never still. Instead, fixational eye movements — small, continuous movements that we are not aware of making — keep them moving even between our voluntary gaze shifts. A new study suggests that involuntary fixational eye movements are more important for vision than previously believed. The ability of humans to perceive the world…
Smallpox Virus Dates Back to Ancient Egyptian Times
Although its origins are still unclear, smallpox was once one of humanity’s most devastating diseases. Historical records and scientific theories about when the smallpox virus first appeared have been at odds for years. A new study shows that the virus is 2,000 years older than scientists had previously suggested. This agrees with historical sources and…
Organelles Develop From Building Blocks In Random Bursts
Eukaryotic cells are highly structured objects that make up the majority of life as we know it, including all animals, plants, and fungi. These cells build and maintain their own internal components, such as membrane-bound organelles like nuclei, which store genetic information, or mitochondria, which produce chemical energy. However, much remains unknown about how they…
Retroviral Gene Fragments Can Destabilize Embryonic Cells
Unexpected effects on embryonic development are caused by ancient, dormant sequences in the genome. This is because retroviral sequences that are mostly “harmless” yet undead are present in the mammalian genome. Recently, some of these retroviral gene fragments’ potential effects on embryonic cells were discovered by an international research team. Unexpectedly, an imbalance in the…
Genetic Mechanism Of Dopamine In Schizophrenia Identified
Schizophrenia is a devastating brain disorder characterized by delusional thinking, hallucinations, and other forms of psychosis; how the brain chemical dopamine relates to this disorder has been a mystery for more than 70 years, but researchers at the Lieber Institute for Brain Development (LIBD) believe they have found an answer. Scientists identified the genetic mechanism…
Kinesin-5 Gene May Protect Against Alzheimer’s Disease
According to a new study, cognitive decline in both mice and humans with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may be protected by the overexpression of a gene linked to cell division and the structure and function of neurons. The gene Kinesin-5 or KIF11 accomplishes this despite the fact that amyloid beta, the main component of plaques in…